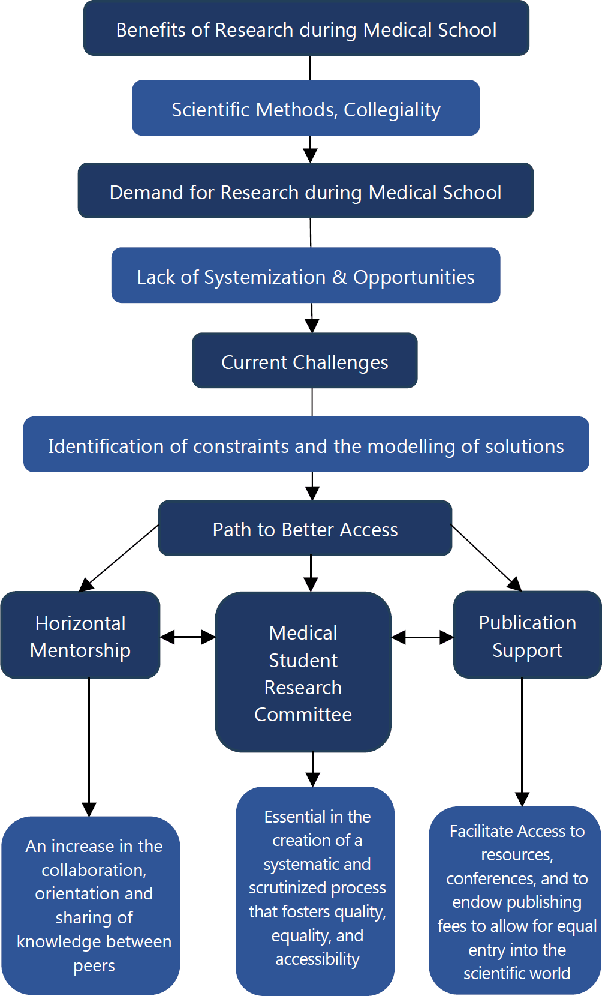
Flowchart on Some of the Proposed Changes and their Intertwining.
José Rodrigues Gomes1
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5195/ijms.2024.2202
Volume 12, Number 2: 222-225
Received 02 10 2023; Rev-request 14 09 2023; Rev-recd 17 09 2023; Accepted 06 05 2024
Flexner's 1910 report was one of the first landmarks in the establishment of scientific research as a pilar of medical curricula. Research as a medical student can be a strenuous task, as the typical curriculum can be incredibly challenging in itself, and the increase in workload associated with research can make it difficult for students to find a healthy balance alongside their social and personal lives, which can lead to serious conditions of stress.1 This often results in students shying away from research, as often they cannot dedicate themselves to proper research projects within their medical faculty. Currently, there is a shrinking number of physician-scientists, resulting in a considerable loss of scientific potential, especially within the translational research realm.2 Some of the most significant breakthroughs in medicine have been accomplished by medical students, such as the discovery of heparin by Jay McLean or the sinoatrial node by Martin Flack. And even though a completely different scientific context is acknowledged for these instances, they still emphasize the need for young, proactive, and committed individuals who offer new perspectives.
There are many reasons why research as a medical student is critical, such as a better understanding of the varying scientific methods, learning to build a passion for a subject, having the opportunity to attend conferences as well the networking and social skills which ultimately help build a robust curriculum vitae (CV). Many of which have already been previously addressed more in depth at the International Journal of Medical Students.2 I have been fortunate enough to be included into my faculty's Cardiovascular Research Unit since my first year. Since then, I have massively improved upon my teamwork and time management skills as well as my work ethic within an academic setting. As I found more opportunities to study and start serving within the unit, I have been able to develop a greater capacity to apprehend and narrate new and often more complex information. I feel this type of experience has been pivotal when deciding to further pursue academic studies, as it has allowed me to discuss and exchange viewpoints with several of my mentors and help me plan to take the best routes to meet my objectives. Students who participated in research projects during medical school were over three times and six times more likely to report interest in research involvement during their future careers and to pursue an academic career, respectively.3,4,5
However, I believe these opportunities are still not well systematized into the typical medical curriculum, especially within my home country of Portugal, even though there is a clear demand for them. An estimated 72% of medical students stated that they wanted to perform research, with 31% reporting an interest in actively engaging in research throughout their career.2 For example, at the College of Medicine, King Saud bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences in Saudi Arabia, a survey showed that a large majority of students (79.8%) affirmed the significance of research in the identification and exploration of issues within a subject matter.5 Additionally, over half of the students (63.6%), expressed keen interest in engaging in research activities during their undergraduate studies. Among the factors driving participation in medical research, the most prominent were the desire to enhance prospects for entry into competitive residency programs, followed by a specific interest in research fields or medical topics, and the aim to bolster one's CV.5 Therefore, the need to create more opportunities is critical, and must be directly addressed. Admittedly, several attempts have been made, for example in the U.K, through the incorporation of student-selected components7, the intercalation of a year in research6 (alongside the typical Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery), or in the U.S. through more ample research and medical curriculums9 (e.g., “The Discovery Curriculum” at Stanford). However, the statistics show that we are still lacking, as for example only 14% of students in U.K. medical schools had submitted an article for publication at the end of their medical degree, and only 22% of students believed they had been taught how to properly write a scientific paper.10 Therefore, current medical curriculums are still not adapted towards the needs and wants of their students, resulting in low adhesion rates. As discussed with colleagues in both my country and others within the EU, the consensus is that there is still a shortage of mentorship, time, and opportunities to conduct research beside the standard medical curriculum.
The sooner medical students are integrated into research, the greater the probability of developing long-lasting physician-scientists.11 By accommodating to this context, it is probable that we have to move away from more conservative and didactic approaches and offer students the opportunity to pursue their interests through a more progressive curriculum that allows for greater flexibility, which has already been referenced by the Comission on Education of Health Professionals for the 21st Century.12
Recognizing my lack of perspective concerning the insufficient access to research for medical students in the Global South and the issues specific to their context, it is my sincere hope that this acknowledgment serves as a catalyst for collective action. By shining a spotlight on this critical gap, I aim to stimulate not only self-reflection but also motivate fellow colleagues and stakeholders to redouble their efforts in implementing comprehensive research initiatives in the Global South. Only through a concerted commitment to addressing these disparities can we pave the way for a more inclusive and impactful medical education system worldwide. Thus, despite their unwavering dedication to the medical profession, many aspiring doctors in the Global South find their educational journey marred by a significant dearth of access to essential research materials, impeding their ability to stay abreast of cutting-edge medical advancements and hindering the development of a more robust academic foundation. Acknowledging this disparity is a vital step towards fostering a more equitable and inclusive educational landscape, ensuring that aspiring healthcare professionals worldwide have equal opportunities to engage with the latest medical knowledge and contribute meaningfully to the field.
Although changing medical curriculums is a demanding and time-consuming task that takes many years to be fully completed, there are quick and practical measures that can be better implemented. As highlighted recently, horizontal mentorship arrangements might aid upcoming students to feel more contented asking peers questions, which enables companionship among colleagues and raises communication standards.13 From personal experience, this is vital as it allows for discussion between colleagues in different year groups, which otherwise would not interconnect and allows for the passage of valuable knowledge. Or through the creation of a medical student research committee, which has already shown to dramatically increase student participation in research and substantially increase both inter- and intra-department communication, and aid in the dissemination of student research as a whole.14 These measures are fundamental, as most students remain largely uninformed about research projects performed at their medical faculty.15 Among other forms of support, research departments should also include quotas in order to support students that face publication charges or through new strategies that motivate principal investigators (PIs) to accommodate more undergraduate pupils in their labs (increase lab's budgets, PIs that accept more undergraduate students have a greater input in decisions related to the school's medical curriculum).
Figure 1.Flowchart on Some of the Proposed Changes and their Intertwining.

Practically implementing the proposed changes in medical curricula involves a systematic approach. To initiate horizontal mentorship arrangements, the identification of willing mentors, development of a structured program, and orientation sessions for both mentors and mentees are key steps. For the creation of a medical student research committee, it is essential to form a dedicated committee, define clear objectives, conduct training workshops, and ensure seamless integration with department structures. Addressing publication challenges through quotas and incentivizing PIs involves collaboration with the administration, introducing financial support, and communicating the benefits of student involvement. To raise awareness, incorporate information about these initiatives in orientation programs, maintain regular communication channels, and encourage faculty engagement. Continuous evaluation through feedback loops and the adaptation of strategies based on insights will ensure the ongoing effectiveness of these changes. By carefully implementing these practical measures, the proposed changes can be integrated into the medical education system, fostering a collaborative and research-oriented environment that enhances the overall learning experience for students.
However, it is crucial to anticipate and address potential counterarguments to these proposed changes and implementations. As for example, concerns about resource constraints, asserting that the allocation of additional resources for such initiatives may be impractical given tight institutional budgets. Another counterargument could center on the perceived limited impact of these measures on the overall medical education course, contending that while beneficial for fostering community and research participation, they might not directly enhance the fundamental medical education & research objectives. Resistance to change within established systems may pose a significant hurdle, as faculty and administrators may resist alterations perceived as disrupting traditional structures. Skepticism about the effectiveness of quotas to support students and concerns about compromising the quality of research by encouraging PIs to accommodate more undergraduate students may also be raised. Additionally, critics might question the potential impact on time-intensive clinical training and express sustainability concerns, suggesting that the initial enthusiasm for these measures may diminish over time. Effectively addressing these counterarguments is essential to build a compelling case for the proposed changes, emphasizing their potential benefits while alleviating concerns about feasibility, impact, and sustainability.
I can testify that the integration into my research group has been extremely gratifying, as it offered an additional purpose to my academic life and has made me feel even more worthwhile within my faculty. Together with this, it has aided in opening new academic opportunities, which would have remained largely unavailable if I had not accepted this undertaking. In conclusion, it is essential that students have at their disposal the proper external motivators, such as faculty guidance, distinction, and sustenance, to allow for junior medical research to be conducted appropriately. As this will show that research, is not an overwhelmingly commitment but rather a rewarding and dignifying one.
None
The Authors have no funding, financial relationships or conflicts of interest to disclose.
Conceptualization: JRG. Investigation: JRG. Writing - Review Editing: JRG.
1. Bergmann C, Muth T, Loerbroks A. Medical students' perceptions of stress due to academic studies and its interrelationships with other domains of life: a qualitative study. Med Educ Online. 2019;24(1):1603526–1603526.
2. Bonilla-Vélez J, Small M, Urrutia R, Lomberk G. The enduring value of research in medical education. Int J Med Stud. 2017;5(1):37–44.
3. Amgad M, Man Kin Tsui M, Liptrott SJ, Shash E. Medical Student Research: An Integrated Mixed-Methods Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLos One. 2015;10(6):e0127470.
4. Frishman WH. Student research projects and theses: should they be a requirement for medical school graduation? Heart Dis. May-Jun 2001;3(3):140–4.
5. Solomon SS, Tom SC, Pichert J, Wasserman D, Powers AC. Impact of medical student research in the development of physician-scientists. J Investig Med. 2003;51(3):149–56.
6. AlRajhi B, Omer I, Abualnaja R, Alqahtani F, Hakami AY. Medical Students' Attitudes and Influential Factors Towards Conducting Medical Research. Int J Med Stud. 2023;11(1):45–51
7. Richardson J, Woolf K, Potts HWW, Bark P, Gill D. What influences medical students' choice of Student Selected Component? The relationship between sex, personality, motivation and SSC choice in first year medical students. Med Teach. 2009;31(9), e418–24
8. Agha R, Fowler A, Whitehurst K, Rajmohan S, Gundogan B, Koshy K. Why apply for an intercalated research degree? Int J Surg Oncol (NY). 2017;2(6):e27.
9. Ringsted C, Hodges B, Scherpbier A. ‘The research compass’: an introduction to research in medical education: AMEE Guide no. 56. Med Teach. 2011;33(9):695–709.
10. Griffin MF, Hindocha S. Publication practices of medical students at British medical schools: Experience, attitudes and barriers to publish. Med Teach. 2011;33(1):e1–e8.
11. Reinders JJ, Kropmans TJ, Cohen-Schotanus J. Extracurricular research experience of medical students and their scientific output after graduation. Med Educ. 2005;39(2):237.
12. Frenk J, Chen L, Bhutta ZA, et al. Health professionals for a new century: transforming education to strengthen health systems in an interdependent world. Lancet. 2010;376(9756):1923–58.
13. Zheng DX. The Need for Horizontal Mentorship Networks to Facilitate Medical Students’ Engagement in Research. Acad Med. 2022;97(2):167–169.
14. Schexnayder S, Starring H, Fury M, Mora A, Leonardi C, Dasa V. The formation of a medical student research committee and its impact on involvement in departmental research. Med Educ Online. 2018;23(1):1424449.
15. Burgoyne LN, O'Flynn S, Boylan GB. Undergraduate medical research: the student perspective. Med Educ Online. 2010;15(1):5212.
José Rodrigues Gomes, 1 Fourth-year medical student at the School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences Abel Salazar, University of Porto.
About the Author: José Rodrigues Gomes is a fourth-year medical student at the School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences Abel Salazar, University of Porto. Currently, I he is a Junior Researcher at the Unit for Multidisciplinary Biomedical. His academic focus lies in cardiovascular physiology and pathology, with a particular interest in their association to obesity. Beyond research, he is passionate about medical education, healthcare management, and sustainable clinical practices, envisioning a future where healthcare aligns with ecological responsibility.
Correspondence: José Rodrigues Gomes. Address: Rua de Jorge Viterbo Ferreira, 228 4050-313 Porto. Email: josemanuelrgomes@gmail.com
Editor: Francisco J. Bonilla-Escobar; Student Editors: Praise Senyuy Wah & Moez Bashir; Copyeditor: Sohaib Haseeb; Proofreader: Laeeqa Manji; Layout Editor: Julián A. Zapata-Ríos; Process: Peer-reviewed
Cite as Rodrigues-Gomes J. Conducting Research as a Medical Student: A Need for Change. Int J Med Stud. 2024 Apr-Jun;12(2):222-225.
Copyright © 2024 José Rodrigues Gomes
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
International Journal of Medical Students, VOLUME 12, NUMBER 2, May 2024