The Role and Impact of Dyslexia Awareness Workshops in the Medical Curriculum
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5195/ijms.2023.1486Keywords:
Medical Education, Undergraduate, Dyslexia, Awareness, Workshop, MD, MBBS, Medical student, MD-PhD, MD-MSc, DO, Curriculum, Curriculum Development, Medical Curriculum, Learning Disabilities, Reading, Writing, DisabilityAbstract
Background: To increase recognition of the number of students who study medicine with dyslexia and the support available, it is important to cultivate a culture in which peers can support fellow peers with dyslexia academically and pastorally. This study aims to understand medical students’ perceptions of dyslexia and confidence with supporting fellow peers with dyslexia before and after a workshop on dyslexia.
Method: Pre-Post Intervention Evaluation form of 36 1st year medical students before the start of a small group dyslexia awareness session and one month after using a standardized 36 True/False/Don’t know questionnaire to elicit any significant change in knowledge about dyslexia. A standardized 6-item Likert Scale questionnaire was also administered in the same time frame to measure confidence in supporting peers with dyslexia.
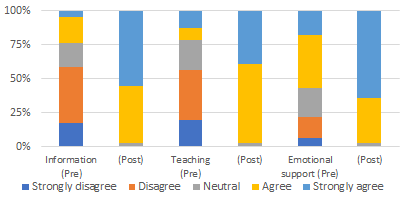
Results: Pre-dyslexia awareness workshop, the mean score on the knowledge and beliefs about dyslexia questionnaire was 15.22, post-intervention this improved to 24.03 (p<0.001). Additionally, pre-intervention greater than 70% of participants reported feeling not confident in items in the confidence questionnaire associated with supporting dyslexia peers academically or signposting to reasonable adjustments and further support. This changed post-intervention with greater than 88% agreeing or strongly agreeing with these items.
Conclusion: At a baseline level, medical students have less precise accuracy in knowledge and beliefs about dyslexia and are not confident in supporting dyslexia peers academically. The findings suggest that dyslexia awareness workshops in the medical curriculum have benefits in increasing knowledge about dyslexia and providing students with confidence in supporting their fellow peers with dyslexia.
References
British Medical Association. Equality and diversity in UK medical schools. Equality and diversity in UK medical schools. Available from: https://www.nuffieldtrust.org.uk/files/2019-11/1575040339_bmastudentreport2009.pdf. Last updated Oct 1, 2009; cited Mar 5, 2021.
GOV.UK. Understanding Disabilities and Impairments. Simone: dyslexic user. Available from: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/understanding-disabilities-and-impairments-user-profiles/simone-dyslexic-user#:~:text=Include%20Us%20All-,Statistics%20about%20dyslexia,an%2011%2Dyear%2Dold. Last updated Oct 25, 2017; cited Mar 5, 2021.
International Classification of Disease version 10th Classifications of Mental and Behavioural Disorder: Clinical Descriptions and Diagnostic Guidelines. Geneva. World Health Organization. 1992
British Dyslexia Association. How is dyslexia diagnosed? Available from: https://www.bdadyslexia.org.uk/dyslexia/how-is-dyslexia-diagnosed/dyslexia-diagnostic-assessment. Last updated Jan 30, 2010; Cited Apr 1, 2021.
Carter C, Sellman E. A view of dyslexia in context: Implications for understanding differences in essay writing amongst higher education students identified as dyslexic. Dyslexia. 2013;19(3):149-64. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/dys.1457
Shaw S, Malik M, Anderson J. The exam performance of medical students with dyslexia: a review of the literature. Med Ed Publish. 2017;6(3):2. DOI: https://doi.org/10.15694/mep.2017.000116
Pino M, Mortari L. The Inclusion of Students with Dyslexia in Higher Education: A systematic review using narrative synthesis. Dyslexia. 2014;20(4):346-69. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/dys.1484
Mckendree J, Snowling MJ. Examination results of medical students with dyslexia. Med Educ. 2011;45(2):176-82. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2923.2010.03802.x
Ghisi M, Bottesi G, Re AM, Cerea S, Mammarella IC. Socioemotional Features and Resilience in Italian University Students with and without Dyslexia. Front Psychol. 2016;7:478. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00478
Shaw S, Keith C, Anderson JL. Doctors with dyslexia: a world of stigma, stonewalling and silence, still? Med Ed Publish. 2017;6(1):29. DOI: https://doi.org/10.15694/mep.2017.000029
Child J, Langford E. Exploring the learning experiences of nursing students with dyslexia. Nurs Stand. 2011;25(40):39-46. DOI: https://doi.org/10.7748/ns2011.06.25.40.39.c8565
Morris D, Turnball P. Clinical experiences of students with dyslexia. J. Adv. Nurs. 2006;54(2):238-47. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.2006.03806.x
Andre C, Deerin J, Leykum L. Students helping students: vertical peer mentoring to enhance the medical school experience. BMC Res Notes. 2017;10(1):176. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-017-2498-8
Akinla O, Hagan P, Atiomo W. A systematic review of the literature describing the outcomes of near-peer mentoring programs for first year medical students. BMC Med Educ. 2018;18(1):98. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-018-1195-1
Soriano-Ferrer M, Echegary-Bengoa JA. A Scale of Knowledge and Beliefs about Developmental Dyslexia: Scale Development and Validation. Procedia Soc Behav Sci. 2014;132:203-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.04.299
Soriano-Ferrer M, Echegaray-Bengoa J, Joshi R. Knowledge, and beliefs about developmental dyslexia in pre-service and in-service Spanish-speaking teachers. Ann of Dyslexia. 2015;66(1):91-110. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-015-0111-1
Sümer Dodur H, Altindağ Kumaş Ö. Knowledge and beliefs of classroom teachers about dyslexia: the case of teachers in Turkey. Eur J Spec Needs Educ. 2020;36(4):593-609. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/08856257.2020.1779980
Schabmann A, Eichert H, Schimdt BM, Hennes A, Ramacher-Faasen N. Knowledge, awareness of problems, and support: university instructors' perspectives on dyslexia in higher education. Eur J Spec Needs Educ. 2020;35(2):273-82. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/08856257.2019.1628339
Ryder D, Norwich B. What's in a name? Perspectives of dyslexia assessors working with students in the UK higher education sector. Dyslexia 2018;24(2):109-27. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/dys.1582
Knight C. What is dyslexia? An exploration of the relationship between teachers' understandings of dyslexia and their training experiences. Dyslexia 2018;24(3):207-19. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/dys.1593
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Mitchell Osei-Junior, Mayya Vorona

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- The Author retains copyright in the Work, where the term “Work” shall include all digital objects that may result in subsequent electronic publication or distribution.
- Upon acceptance of the Work, the author shall grant to the Publisher the right of first publication of the Work.
- The Author shall grant to the Publisher and its agents the nonexclusive perpetual right and license to publish, archive, and make accessible the Work in whole or in part in all forms of media now or hereafter known under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License or its equivalent, which, for the avoidance of doubt, allows others to copy, distribute, and transmit the Work under the following conditions:
- Attribution—other users must attribute the Work in the manner specified by the author as indicated on the journal Web site; with the understanding that the above condition can be waived with permission from the Author and that where the Work or any of its elements is in the public domain under applicable law, that status is in no way affected by the license.
- The Author is able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the nonexclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the Work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), as long as there is provided in the document an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post online a prepublication manuscript (but not the Publisher’s final formatted PDF version of the Work) in institutional repositories or on their Websites prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work. Any such posting made before acceptance and publication of the Work shall be updated upon publication to include a reference to the Publisher-assigned DOI (Digital Object Identifier) and a link to the online abstract for the final published Work in the Journal.
- Upon Publisher’s request, the Author agrees to furnish promptly to Publisher, at the Author’s own expense, written evidence of the permissions, licenses, and consents for use of third-party material included within the Work, except as determined by Publisher to be covered by the principles of Fair Use.
- The Author represents and warrants that:
- the Work is the Author’s original work;
- the Author has not transferred, and will not transfer, exclusive rights in the Work to any third party;
- the Work is not pending review or under consideration by another publisher;
- the Work has not previously been published;
- the Work contains no misrepresentation or infringement of the Work or property of other authors or third parties; and
- the Work contains no libel, invasion of privacy, or other unlawful matter.
- The Author agrees to indemnify and hold Publisher harmless from the Author’s breach of the representations and warranties contained in Paragraph 6 above, as well as any claim or proceeding relating to Publisher’s use and publication of any content contained in the Work, including third-party content.
Enforcement of copyright
The IJMS takes the protection of copyright very seriously.
If the IJMS discovers that you have used its copyright materials in contravention of the license above, the IJMS may bring legal proceedings against you seeking reparation and an injunction to stop you using those materials. You could also be ordered to pay legal costs.
If you become aware of any use of the IJMS' copyright materials that contravenes or may contravene the license above, please report this by email to contact@ijms.org
Infringing material
If you become aware of any material on the website that you believe infringes your or any other person's copyright, please report this by email to contact@ijms.org







