Hydatid Cyst Complicated by Dilated Bile Duct Treated with Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): A Case Report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5195/ijms.2025.2517Keywords:
Cholangiopancreatography Endoscopic Retrograde, Echinococcosis, Common Bile DuctAbstract
Background: Echinococcosis, primarily caused by Echinococcus granulosus, frequently leads to the formation of hydatid cysts in various organs, particularly the liver and lungs. In rare instances, these cysts can rupture into the biliary tract, resulting in complications such as dilation of the Common Bile Duct (CBD) and obstructive jaundice. This study aims to document a rare case of CBD dilation due to the rupture of a hydatid cyst, highlighting the need for tailored diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for this unusual presentation.
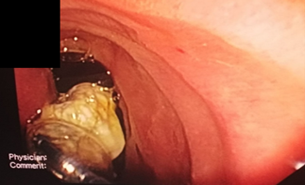
The Case: A 37-year-old male patient presented with abdominal pain, anorexia, and jaundice. Abdominal ultrasonography and computed tomography (CT) scans identified multiple hydatid cysts in the liver, with one ruptured cyst extending into the CBD. An endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) was performed to remove the hydatid cyst membranes, followed by the placement of a stent and irrigation of the biliary ducts. Surgical excision of remaining liver cysts was subsequently conducted. The use of ERCP allowed effective removal of cystic material from the biliary tract, reducing CBD obstruction and alleviating jaundice symptoms. Surgical intervention further ensured the complete removal of hydatid cysts.
Conclusion: This case highlights that Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is an effective diagnostic and therapeutic tool for managing biliary complications associated with hydatid disease, particularly the dilation of the Common Bile Duct (CBD). The combination of ERCP with surgical intervention resulted in optimal outcomes for this patient, who presented an uncommon manifestation of echinococcosis.
References
Smith I., Monkemuller K., and Wilcox C.M. Incidentally Identified Common Bile Duct Dilatation: A Systematic Review of Evaluation, Causes, and Outcome. J Clin Gastroenterol: 2015. 49(10):810-5.
Holm A.N. and Gerke H. What should be done with a dilated bile duct? Curr Gastroenterol Rep: 2010. 12(2):150-6.
Becker K., Frieling T., Saleh A., and Häussinger D. Resolution of hydatid liver cyst by spontaneous rupture into the biliary tract. J Hepatol: 1997. 26(6):1408-12.
Songür Y., Temuçin G., and Sahin B. Endoscopic ultrasonography in the evaluation of dilated common bile duct. J Clin Gastroenterol: 2001. 33(4):302-5.
Lv Y., Liu N., Wu H., and Li Z. Etiological classification and treatment strategies for secondary bile duct dilatation. Exp Biol Med (Maywood): 2021. 246(3):281-285.
Sanders D.J., Bomman S., Krishnamoorthi R., and Kozarek R.A. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: Current practice and future research. World J Gastrointest Endosc: 2021. 13(8):260-274.
Sen P., Demirdal T., and Nemli S.A. Evaluation of clinical, diagnostic and treatment aspects in hydatid disease: analysis of an 8-year experience. Afr Health Sci: 2019. 19(3):2431-2438.
Mehta P., Prakash M., and Khandelwal N. Radiological manifestations of hydatid disease and its complications. Trop Parasitol: 2016. 6(2):103-112.
Greco S., Cannella R., Giambelluca D., Pecoraro G., Battaglia E., Midiri M., et al. Complications of hepatic echinococcosis: multimodality imaging approach. Insights Imaging: 2019. 10(1):113.
BekÇİ T.T. Diagnosis and treatment of human hydatid disease. European Journal of General Medicine: 2012. 9(12):15-20.
Hamza A., Krasniqi A., Sada F., Zejnullahu V., and Bicaj B. ERCP treatment of obstructive jaundice caused by hydatid cyst in extrahepatic ducts 13 years after liver hydatid endocystectomy. A case report. Int J Surg Case Rep: 2020. 74:38-41.
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ahmad Hmaideh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- The Author retains copyright in the Work, where the term “Work” shall include all digital objects that may result in subsequent electronic publication or distribution.
- Upon acceptance of the Work, the author shall grant to the Publisher the right of first publication of the Work.
- The Author shall grant to the Publisher and its agents the nonexclusive perpetual right and license to publish, archive, and make accessible the Work in whole or in part in all forms of media now or hereafter known under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License or its equivalent, which, for the avoidance of doubt, allows others to copy, distribute, and transmit the Work under the following conditions:
- Attribution—other users must attribute the Work in the manner specified by the author as indicated on the journal Web site; with the understanding that the above condition can be waived with permission from the Author and that where the Work or any of its elements is in the public domain under applicable law, that status is in no way affected by the license.
- The Author is able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the nonexclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the Work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), as long as there is provided in the document an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post online a prepublication manuscript (but not the Publisher’s final formatted PDF version of the Work) in institutional repositories or on their Websites prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work. Any such posting made before acceptance and publication of the Work shall be updated upon publication to include a reference to the Publisher-assigned DOI (Digital Object Identifier) and a link to the online abstract for the final published Work in the Journal.
- Upon Publisher’s request, the Author agrees to furnish promptly to Publisher, at the Author’s own expense, written evidence of the permissions, licenses, and consents for use of third-party material included within the Work, except as determined by Publisher to be covered by the principles of Fair Use.
- The Author represents and warrants that:
- the Work is the Author’s original work;
- the Author has not transferred, and will not transfer, exclusive rights in the Work to any third party;
- the Work is not pending review or under consideration by another publisher;
- the Work has not previously been published;
- the Work contains no misrepresentation or infringement of the Work or property of other authors or third parties; and
- the Work contains no libel, invasion of privacy, or other unlawful matter.
- The Author agrees to indemnify and hold Publisher harmless from the Author’s breach of the representations and warranties contained in Paragraph 6 above, as well as any claim or proceeding relating to Publisher’s use and publication of any content contained in the Work, including third-party content.
Enforcement of copyright
The IJMS takes the protection of copyright very seriously.
If the IJMS discovers that you have used its copyright materials in contravention of the license above, the IJMS may bring legal proceedings against you seeking reparation and an injunction to stop you using those materials. You could also be ordered to pay legal costs.
If you become aware of any use of the IJMS' copyright materials that contravenes or may contravene the license above, please report this by email to contact@ijms.org
Infringing material
If you become aware of any material on the website that you believe infringes your or any other person's copyright, please report this by email to contact@ijms.org







