A Scoping Review on the Utility of Ultrasound to Visualize Bursae in Anatomical Dissection Courses
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5195/ijms.2024.2406Keywords:
Education, Medical, Cadaver, ultrasound, Bursa, synovial , review, Ultrasound, Bursae Visualization, Anatomical Dissection, Sonoanatomy, Cadaver Studies, High-Resolution Imaging, B-Mode Ultrasound, Educational Tool, Grey Literature, Medical EducationAbstract
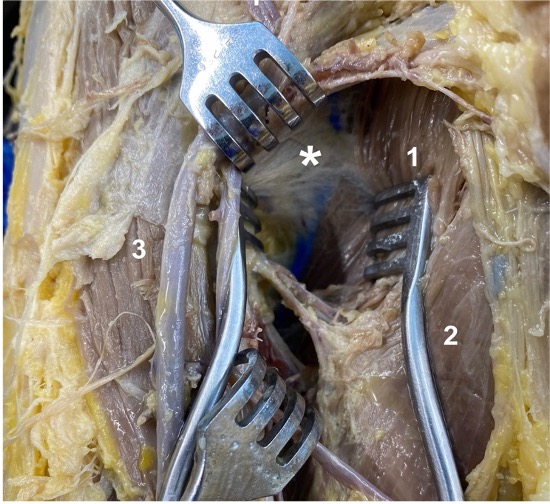
Bursitis is a common condition in clinical practice, often causing pain in the shoulder and buttock areas due to inflamed bursae. Proper diagnosis and treatment depend on knowing the presence and exact location of these bursae. Anatomy classes typically provide limited instruction on bursae because they are difficult to demonstrate during dissection courses. High-resolution ultrasound is an essential and versatile technique for detecting bursitis, and it could also serve as a valuable tool for students to better understand bursae. Relevant studies were screened in the following databases: CENTRAL, MEDLINE, BIOSIS Previews, EMBASE, and Web of Science Core Collection. Grey literature was also considered. Literature was screened on January 3, 2023. Only ultrasound investigations in human cadaver bursae were included, specifically using B-Mode ultrasound. The general characteristics of the included studies and the ultrasound-guided approaches for labeling the bursae were analyzed and examined. T The search found 8,899 matches, but only 15 met the criteria. Fifteen different bursae were studied, and 12 studies were included in the analysis. Both the marking substrate and the injected volume varied. Despite a high overall accuracy of 99% achieved using ultrasound-guided labeling approaches in the included studies, caution is advised due to the small sample size (1 to 24). The current study serves as a review to examine ultrasound studies on bursae in human cadavers. Ultrasound-guided labeling techniques achieve high accuracy and could be a valuable teaching tool in dissection courses. These techniques help visualize difficult-to-dissect structures and provide students with an understanding of sonoanatomy.
References
Monro A. A description of all the bursae mucosae of the human body; their structure explained, and compared with that of the capsular ligaments of the joints, and of those sacs which line the cavities of the thorax and abdomen; with remarks on the accidents and diseases which affect those several sacs, and on the operations necessary for their cure. Edinburgh: Printed for C. Elliot, T. Kay ..., London; and for Charles Elliot, Edinburgh; 1788.
Koudela K, Jr., Koudelová J, Koudela K, Sr., Kunesová M. Bursitis iliopectinea. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2008;75(5):347-54.
Dihlmann W, Peters A, Tillmann B. The bursa iliopectinea--a morphologic-computed tomographic study. Rofo. 1989;150(3):274-9.
Resnick DLK, H. S.; Pretterklieber, M. L. Internal derangements of joints. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2007.
Canoso JJ, Stack MT, Brandt KD. Hyaluronic acid content of deep and subcutaneous bursae of man. Ann Rheum Dis. 1983;42(2):171-5.
Van Mieghem IM, Boets A, Sciot R, Van Breuseghem I. Ischiogluteal bursitis: an uncommon type of bursitis. Skeletal Radiol. 2004;33(7):413-6.
Sawyer E, Varacallo M. Anatomy, shoulder and upper limb, hand ulnar bursa. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing
Copyright © 2023, StatPearls Publishing LLC.; 2023.
Stecco C. Atlas des menschlichen fasziensystems: Elsevier Health Sciences; 2016.
Stecco C, Fede C, Macchi V, Porzionato A, Petrelli L, Biz C, et al. The fasciacytes: A new cell devoted to fascial gliding regulation. Clin Anat. 2018;31(5):667-76.
De Oliveira-Lagôa S, Cruz FB, Azócar DLM, Lavilla EO, Abdala V. Anuran forelimb muscle tendinous structures and their relationship with locomotor modes and habitat use. Curr Zool. 2019;65(5):599-608.
Pujalte G, Hudspeth LJ, Troyer WD, Shapiro SA. Ultrasound-guided injection of the long head of the biceps tendon sheath with concomitant subacromial bursa injection through the same needlestick. Clin Anat. 2022.
Tamborrini G, Marx C. Cme-rheumatology 7: trochanter major pain syndrome. Praxis (Bern 1994). 2016;105(3):172-4.
Tamborrini G, Müller-Gerbl M, Müller SA. Cme-sonography 106: subacromial bursa - a myth. Praxis (Bern 1994). 2022;111(15):833-46.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O'Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467-73.
Gotschall T. EndNote 20 desktop version. J Med Libr Assoc. 2021;109(3):520-2.
Bramer WM, Giustini D, de Jonge GB, Holland L, Bekhuis T. De-duplication of database search results for systematic reviews in EndNote. J Med Libr Assoc. 2016;104(3):240-3.
Dang D, Kamal M, Kumar M, Paliwal B, Nayyar A, Bhatia P, et al. Comparison of human cadaver and blue phantom for teaching ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia to novice postgraduate students of anesthesiology: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of anaesthesiology, clinical pharmacology. 2024;40(2):276‐82.
Stallenberg B, Destate N, Feipel V, Gevenois PA. Involvement of the anterior portion of the subacromial-subdeltoid bursa in the painful shoulder. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006;187(4):894-900.
Aguiar RO, Gasparetto EL, Escuissato DL, Marchiori E, Trudell DJ, Haghighi P, et al. Radial and ulnar bursae of the wrist: cadaveric investigation of regional anatomy with ultrasonographic-guided tenography and MR imaging. Skeletal Radiol. 2006;35(11):828-32.
Aguiar RO, Viegas FC, Fernandez RY, Trudell D, Haghighi P, Resnick D. The prepatellar bursa: cadaveric investigation of regional anatomy with mri after sonographically guided bursography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;188(4):W355-8.
Finnoff JT, Nutz DJ, Henning PT, Hollman JH, Smith J. Accuracy of ultrasound-guided versus unguided pes anserinus bursa injections. PM&R. 2010;2(8):732-9.
Gaetke-Udager K, Jacobson JA, Bhatti ZS, Smith J, Parameswaran A, Fessell DP. Ultrasound of the gruberi bursa with cadaveric and mri correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2016;207(2):386-91.
Moore BJ, Johnson W, Finnoff JT, Smith J, Sellon JL. Distribution of sonographically guided injections of the subgluteus minimus and medius bursae in cadaveric model. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2019;51(6, Suppl. S):592.
Mu A, Peng P, Agur A. Landmark-guided and ultrasound-guided approaches for trochanteric bursa injection: a cadaveric study. Anesth Analg. 2017;124(3):966-71.
Nakase J, Yoshimizu R, Kimura M, Kanayama T, Yanatori Y, Tsuchiya H. Anatomical description and short-term follow up clinical results for ultrasound-guided injection of medial collateral ligament bursa: New conservative treatment option for symptomatic degenerative medial meniscus tear. Knee. 2022;38:1-8.
Norbury JW, Karr NC, Sindhi V, Rathbun KM, Charles SC, McIver MB, et al. Improving the performance time and accuracy of ultrasound-guided interventions: a randomized controlled double-blind trial of the line-of-sight approach and the „apples“ mnemonic. J Ultrasound Med. 2018;37(12):2909-14.
Onishi K, Sellon JL, Smith J. Sonographically guided semimembranosus bursa injection: technique and validation. PM&R. 2016;8(1):51-7.
Pekala PA, Henry BM, Pekala JR, Piska K, Tomaszewski KA. The Achilles tendon and the retrocalcaneal bursa an anatomical and radiological study. Bone Jt Res. 2017;6(7):446-51.
Smith J, Wisniewski SJ, Wempe MK, Landry BW, Sellon JL. Sonographically guided obturator internus injections: techniques and validation. J Ultrasound Med. 2012;31(10):1597-608.
Viegas FC, Aguiar RO, Gasparetto E, Marchiori E, Trudell DJ, Haghighi P, et al. Deep and superficial infrapatellar bursae: cadaveric investigation of regional anatomy using magnetic resonance after ultrasound-guided bursography. Skeletal Radiol. 2007;36(1):41-6.
Wisniewski SJ, Hurdle M, Erickson JM, Finnoff JT, Smith J. Ultrasound-guided ischial bursa injection: technique and positioning considerations. PM&R. 2014;6(1):56-60.
Wu T, Song HX, Dong Y, Li JH. Ultrasound-guided versus blind subacromial-subdeltoid bursa injection in adults with shoulder pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2015;45(3):374-8.
McGill KC, Patel R, Chen D, Okwelogu N. Ultrasound-guided bursal injections. Skeletal Radiol. 2023;52(5):967-78.
Dzulkifli MA, Mustafar MF. The influence of colour on memory performance: a review. Malays J Med Sci. 2013;20(2):3-9.
Hamza A, Radosa J, Meyberg-Solomayer G, Solomayer EF, Takacs Z, Juhasz-Boess I, et al. Trial integration of combined ultrasound and laparoscopy tuition in an undergraduate anatomy class with volunteer participation - a pilot study. Ann Anat. 2019;221:101-7.
O'Keeffe GW, Davy S, Barry DS. Radiologist's views on anatomical knowledge amongst junior doctors and the teaching of anatomy in medical curricula. Ann Anat. 2019;223:70-6.
Bledsoe A, Zimmerman J. Ultrasound: the new stethoscope (point-of-care ultrasound). Anesthesiol Clin. 2021;39(3):537-53.
Hayashi S, Naito M, Kawata S, Qu N, Hatayama N, Hirai S, et al. History and future of human cadaver preservation for surgical training: from formalin to saturated salt solution method. Anat Sci Int. 2016;91(1):1-7.
Wilke HJ, Werner K, Häussler K, Reinehr M, Böckers TM. Thiel-fixation preserves the non-linear load-deformation characteristic of spinal motion segments, but increases their flexibility. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2011;4(8):2133-7.
Eisma R, Lamb C, Soames RW. From formalin to thiel embalming: what changes? One anatomy department's experiences. Clin Anat. 2013;26(5):564-71.
Wolff KD, Kesting M, Mücke T, Rau A, Hölzle F. Thiel embalming technique: a valuable method for microvascular exercise and teaching of flap raising. Microsurgery. 2008;28(4):273-8.
Stecco C, Fantoni I, Macchi V, Del Borrello M, Porzionato A, Biz C, et al. The role of fasciae in civinini-morton's syndrome. J Anat. 2015;227(5):654-64.
Sawhney C, Lalwani S, Ray BR, Sinha S, Kumar A. Benefits and Pitfalls of Cadavers as Learning Tool for Ultrasound-guided Regional Anesthesia. Anesth Essays Res. 2017;11(1):3-6.
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Felix Margenfeld, Adib Zendehdel, Giorgio Tamborrini, Jennifer Polzer, Marc Naville, Amélie Poilliot, Magdalena Müller-Gerbl

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- The Author retains copyright in the Work, where the term “Work” shall include all digital objects that may result in subsequent electronic publication or distribution.
- Upon acceptance of the Work, the author shall grant to the Publisher the right of first publication of the Work.
- The Author shall grant to the Publisher and its agents the nonexclusive perpetual right and license to publish, archive, and make accessible the Work in whole or in part in all forms of media now or hereafter known under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License or its equivalent, which, for the avoidance of doubt, allows others to copy, distribute, and transmit the Work under the following conditions:
- Attribution—other users must attribute the Work in the manner specified by the author as indicated on the journal Web site; with the understanding that the above condition can be waived with permission from the Author and that where the Work or any of its elements is in the public domain under applicable law, that status is in no way affected by the license.
- The Author is able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the nonexclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the Work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), as long as there is provided in the document an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post online a prepublication manuscript (but not the Publisher’s final formatted PDF version of the Work) in institutional repositories or on their Websites prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work. Any such posting made before acceptance and publication of the Work shall be updated upon publication to include a reference to the Publisher-assigned DOI (Digital Object Identifier) and a link to the online abstract for the final published Work in the Journal.
- Upon Publisher’s request, the Author agrees to furnish promptly to Publisher, at the Author’s own expense, written evidence of the permissions, licenses, and consents for use of third-party material included within the Work, except as determined by Publisher to be covered by the principles of Fair Use.
- The Author represents and warrants that:
- the Work is the Author’s original work;
- the Author has not transferred, and will not transfer, exclusive rights in the Work to any third party;
- the Work is not pending review or under consideration by another publisher;
- the Work has not previously been published;
- the Work contains no misrepresentation or infringement of the Work or property of other authors or third parties; and
- the Work contains no libel, invasion of privacy, or other unlawful matter.
- The Author agrees to indemnify and hold Publisher harmless from the Author’s breach of the representations and warranties contained in Paragraph 6 above, as well as any claim or proceeding relating to Publisher’s use and publication of any content contained in the Work, including third-party content.
Enforcement of copyright
The IJMS takes the protection of copyright very seriously.
If the IJMS discovers that you have used its copyright materials in contravention of the license above, the IJMS may bring legal proceedings against you seeking reparation and an injunction to stop you using those materials. You could also be ordered to pay legal costs.
If you become aware of any use of the IJMS' copyright materials that contravenes or may contravene the license above, please report this by email to contact@ijms.org
Infringing material
If you become aware of any material on the website that you believe infringes your or any other person's copyright, please report this by email to contact@ijms.org







