Evaluating Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation Outcomes in Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Impact of Predisposing Conditions in a Retrospective Cohort
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5195/ijms.2025.2796Keywords:
Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation, Obstructive Sleep Apnea, Patient Outcomes, Comorbid Conditions, Sleep-Related Comorbidities, Polysomnography, CPAP Intolerance, Personalized Treatment, Clinical Benefits, Predictive FactorsAbstract
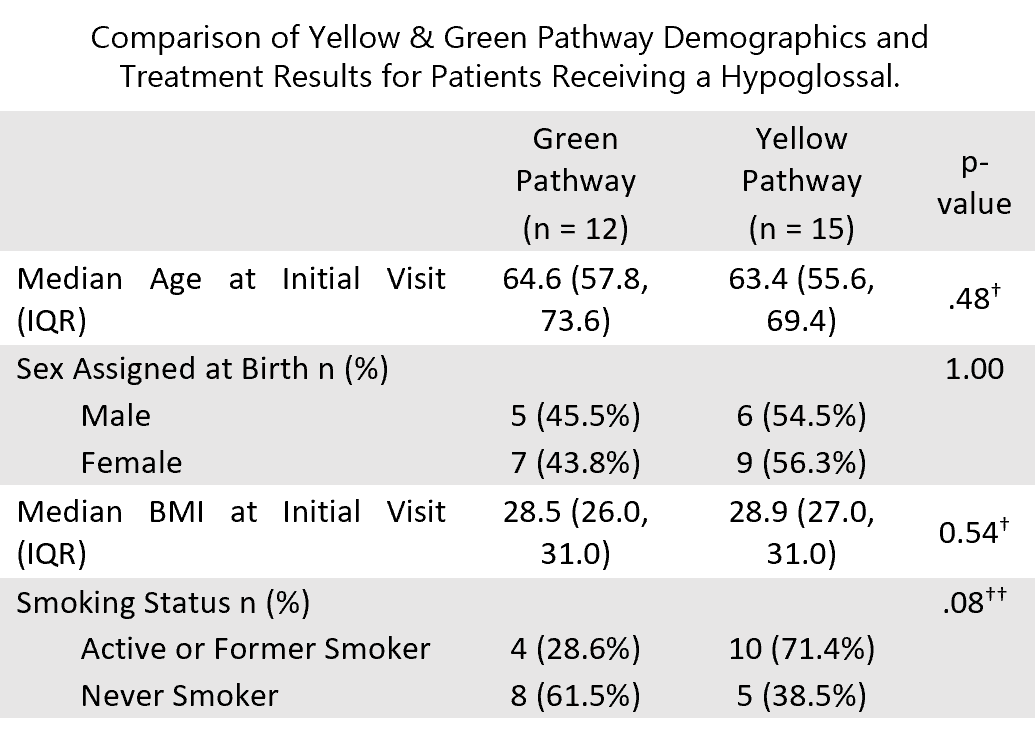
Background: This retrospective study aimed to analyze treatment outcomes for patients receiving a hypoglossal nerve stimulation (HNS) device for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Methods: Chart reviews were conducted for HNS patients who underwent a post-implantation polysomnography (PSG) (typically performed approximately 2 months after device activation) to assess therapeutic response and optimize stimulation settings. Patients were categorized into “green (GP)” (optimal response: AHI <15, ≥4 hours/night device use, and subjective benefit) and “yellow (YP)” (suboptimal response: failure to meet one or more of these criteria) response pathways. Results: Out of 111 patients assessed, 27 patients met pathway categorization criteria. 12 of those were classified in green and 15 in yellow. Median age and BMI were 63.9 years and 28.7 kg/m², respectively, with a balanced sex assigned at birth distribution. HNS treatment reduced median AHI by 85.6% (from 34.7 to 5.0) for the green pathway (GP), and by 87.4% (from 39.6 to 5.0) for the yellow pathway (YP). Patients who had at least one sleep-related comorbidity were more likely to be in the yellow pathway (p < .001). Comorbidities such as depression and insomnia were significantly associated with suboptimal treatment response (yellow pathway) (p = .003 and p = .02, respectively). Conclusions: This study emphasizes the significance of sleep-related comorbidities as a strong predictor of patient outcomes. More efficient utilization of resources may be achieved by considering comorbid conditions prior to HNS implantation. Given the small sample size and retrospective single-institution design, these findings should be interpreted with caution and may not be generalizable to broader populations.
References
Ghavami T, Kazeminia M, Ahmadi N, Rajati F. Global Prevalence of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in the Elderly and Related Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Study. J Perianesth Nurs. 2023;38(6):865-875.
Lin HS, Prasad AS, Pan CJ, Rowley JA. Factors associated with noncompliance to treatment with positive airway pressure. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007;133(1):69-72.
Qiao M, Xie Y, Wolff A, Kwon J. Long term adherence to continuous positive Airway pressure in mild obstructive sleep apnea. BMC Pulm Med. 2023;23(1):320.
Schwartz AR, Jacobowitz O, Eisele DW, et al. Targeted Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation for Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Randomized Clinical Trial [published correction appears in JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024 Jun 1;150(6):530. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2024.0412]. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2023;149(6):512-520.
Strollo PJ Jr, Rogers RM. Obstructive sleep apnea. N Engl J Med. 1996;334(2):99-104.
Sawyer AM, Gooneratne NS, Marcus CL, Ofer D, Richards KC, Weaver TE. A systematic review of CPAP adherence across age groups: clinical and empiric insights for developing CPAP adherence interventions. Sleep Med Rev. 2011;15(6):343-356.
Baillieul S, Dekkers M, Brill AK, et al. Sleep apnoea and ischaemic stroke: current knowledge and future directions. Lancet Neurol. 2022;21(1):78-88.
Kirsch DB. Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2020;26(4):908-928.
Bouzerda A. Risque cardiovasculaire et syndrome d’apnées obstructives du sommeil [Cardiovascular risk and obstructive sleep apnea]. Pan Afr Med J. 2018;29:47.
Hobzova M, Prasko J, Vanek J, et al. Depression and obstructive sleep apnea. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2017;38(5):343-352.
Malhotra A. Hypoglossal-nerve stimulation for obstructive sleep apnea. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(2):170-171.
Tukanov E, Van Loo D, Dieltjens M, Verbraecken J, Vanderveken OM, Op de Beeck S. Baseline Characteristics Associated with Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation Treatment Outcomes in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Systematic Review. Life (Basel). 2024;14(9):1129. Published 2024 Sep 7.
Soose, RJ, Faber, K, Greenberg H, Boon M, Woodson T, Strollo P. (2021). Post-implant care pathway: lessons learned and recommendations after 5 years of clinical implementation of hypoglossal nerve stimulation therapy. Sleep, 44(Suppl 1): S4–S10.
Steffen A, Baptista P, Ebner EM, Jeschke S, König IR, Bruchhage KL. Insomnia affects patient-reported outcome in sleep apnea treated with hypoglossal nerve stimulation. Laryngoscope Investigative Otolaryngology. 2022;7(3):877–884.
Pordzik J, Ludwig K, Seifen C, Huppertz T, Bahr-Hamm K, Matthias C, Gouveris H. Insomnia in Patients Undergoing Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation Therapy for Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Biology. 2023;12(1):98.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Lina Adwer

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- The Author retains copyright in the Work, where the term “Work” shall include all digital objects that may result in subsequent electronic publication or distribution.
- Upon acceptance of the Work, the author shall grant to the Publisher the right of first publication of the Work.
- The Author shall grant to the Publisher and its agents the nonexclusive perpetual right and license to publish, archive, and make accessible the Work in whole or in part in all forms of media now or hereafter known under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License or its equivalent, which, for the avoidance of doubt, allows others to copy, distribute, and transmit the Work under the following conditions:
- Attribution—other users must attribute the Work in the manner specified by the author as indicated on the journal Web site; with the understanding that the above condition can be waived with permission from the Author and that where the Work or any of its elements is in the public domain under applicable law, that status is in no way affected by the license.
- The Author is able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the nonexclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the Work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), as long as there is provided in the document an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post online a prepublication manuscript (but not the Publisher’s final formatted PDF version of the Work) in institutional repositories or on their Websites prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work. Any such posting made before acceptance and publication of the Work shall be updated upon publication to include a reference to the Publisher-assigned DOI (Digital Object Identifier) and a link to the online abstract for the final published Work in the Journal.
- Upon Publisher’s request, the Author agrees to furnish promptly to Publisher, at the Author’s own expense, written evidence of the permissions, licenses, and consents for use of third-party material included within the Work, except as determined by Publisher to be covered by the principles of Fair Use.
- The Author represents and warrants that:
- the Work is the Author’s original work;
- the Author has not transferred, and will not transfer, exclusive rights in the Work to any third party;
- the Work is not pending review or under consideration by another publisher;
- the Work has not previously been published;
- the Work contains no misrepresentation or infringement of the Work or property of other authors or third parties; and
- the Work contains no libel, invasion of privacy, or other unlawful matter.
- The Author agrees to indemnify and hold Publisher harmless from the Author’s breach of the representations and warranties contained in Paragraph 6 above, as well as any claim or proceeding relating to Publisher’s use and publication of any content contained in the Work, including third-party content.
Enforcement of copyright
The IJMS takes the protection of copyright very seriously.
If the IJMS discovers that you have used its copyright materials in contravention of the license above, the IJMS may bring legal proceedings against you seeking reparation and an injunction to stop you using those materials. You could also be ordered to pay legal costs.
If you become aware of any use of the IJMS' copyright materials that contravenes or may contravene the license above, please report this by email to contact@ijms.org
Infringing material
If you become aware of any material on the website that you believe infringes your or any other person's copyright, please report this by email to contact@ijms.org







