Evaluating Medical Students' Knowledge of Medical Malpractice: A Pilot Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5195/ijms.2023.1576Keywords:
Medical malpractice, Physician involvement in malpractice suits, Surgeons and malpractice claims, Medical malpractice insurance premiums, Perception of medical malpractice by medical students, Medico-legal education, Lack of legal education in medical curriculum, Impact of medical malpractice education on students, Global lack of medical malpractice education, Training and education in legal liability, Survey methodology, Baseline medical student knowledge, Questionnaire development, Evaluation of medical malpractice knowledge, Cross-sectional study, Statistical analysis, Stratification of data by demographic factors, Gaps in medico-legal knowledge among medical students, Concerns of medical students regarding malpractice lawsuits, Educational material for medical studentsAbstract
Introduction: Although medical malpractice lawsuits are common and have a tremendous financial and psychological impact on physicians, education about medical malpractice is almost non-existent in most medical school curricula around the world. Nonetheless, medical students are concerned about looming legal lawsuits during their careers and have expressed desire to become educated. The objective of the present study is to evaluate and gauge baseline medico-legal knowledge of medical students.
Methods: A survey with 25 multiple-choice quiz questions regarding malpractice risks, standards of care, and malpractice premiums was prepared with information obtained from peer-reviewed articles after a thorough literature review failed to produce a validated questionnaire for medical students. The survey was distributed to medical students across 5 consecutive years at our medical school, totaling 420 students. Data from the survey was collected via Qualtrics before undergoing statistical analysis.
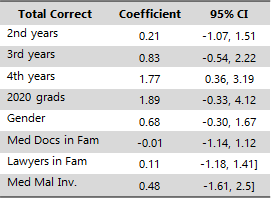
Results: The completion rate for the survey was 110/420 (26.2%). The results showed that no group of students scored greater than 50% correct on the survey, with an overall median score of 40% correct for all students combined. Fourth year medical students correctly answered 1.77 more questions, on average, than first year medical students. There were no statistically significant differences in survey score between students with a personal or familial medical malpractice involvement.
Discussion: The results are an indication that students are not well-educated about medical malpractice, and that medical malpractice education should be implemented in medical school to help prepare future physicians to protect their patients and hopefully avoid malpractice lawsuits.
References
Guardado JR. Medical liability claim frequency among U.S. physicians. American Medical Association. Available from: https://www.ama-assn.org/sites/ama-assn.org/files/corp/media-browser/public/government/advocacy/policy-research-perspective-medical-liability-claim-frequency.pdf. Cited Mar 1, 2023.
Jena AB, Seabury S, Lakdawalla D, Chandra A. Malpractice risk according to physician specialty. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(7):629-36. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMsa1012370
American Medical Association. Medical liability claim frequency among U.S. physicians. Available from: https://www.ama-assn.org/media/21976/download. Cited Sep 26, 2020.
Guardado JR. Prevalence of medical liability premium increases unseen since 2000s continues for third year in a row. American Medical Association. Available from: https://www.ama-assn.org/practice-management/sustainability/nearly-30-medical-liability-insurance-premiums-rose-2021. Cited Mar 1, 2023.
Kelly ET, Miller EA. Perceptions of medical malpractice and medical malpractice reform among first- and fourth-year medical students. Health Policy. 2009;91(1):71-78. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healthpol.2008.11.005
Johnston WF, Rodriguez RM, Suarez D, Fortman J. Study of medical students' malpractice fear and defensive medicine: a "hidden curriculum?". West J Emerg Med. 2014;15(3):293-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5811/westjem.2013.8.19045
Persad GC, Elder L, Sedig L, Flores L, Emanuel EJ. The current state of medical school education in bioethics, health law, and health economics. J Law Med Ethics. 2008;36(1):89-4. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1748-720X.2008.00240.x
Dolin G, Ram N. One model of collaborative learning for medical and law students at the University of Baltimore and Johns Hopkins University. AMA J Ethics. 2016;18(3):237-42. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1001/journalofethics.2016.18.3.medu1-1603
Annandale E, Cunningham-Burley S. Medical students' perceptions of medical malpractice. Med Educ. 1996;30(4):253-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2923.1996.tb00826.x
Al-Azri NH. Providing Legal Education for Medical Students in Arab Gulf Cooperation Council Countries. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2020;7:2382120520928386 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/2382120520928386
Kurban NK, Savaş H, Cetinkaya B, Turan T, Kartal A. Evaluation of nursing students' training in medical law. Nurs Ethics. 2010;17(6):759-68. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0969733010378931
Bono MJ, Wermuth HR, Hipskind JE. Medical malpractice. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing.
HG Legal Resources. Who's liable when medical students make mistakes? Available from: https://www.hg.org/legal-articles/who-s-liable-when-medical-students-make-mistakes-40865. Cited Aug 24, 2021.
Medical Malpractice Help. Who can be sued for medical malpractice? Available from: https://www.medicalmalpracticehelp.com/faqs/who-can-be-sued-for-medical-malpractice/. Cited Aug 24, 2021.
Schaffer AC, Jena AB, Seabury SA, Singh H, Chalasani V, Kachalia A. Rates and characteristics of paid malpractice claims among US physicians by specialty, 1992-2014. JAMA Intern Med. 2017;177(5):710-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.0311
American Bar Association. New ABA data reveals rise in number of U.S. lawyers, 15 percent increase since 2008. Available from: https://www.americanbar.org/news/abanews/aba-news-archives/2018/05/new_aba_data_reveals/. Last updated May 11, 2018; cited August 24, 2021.
Katz ED. Defensive medicine: a case and review of its status and possible solutions. Clin Pract Cases Emerg Med. 2019;3(4):329-32. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5811/cpcem.2019.9.43975
Rothberg MB, Class J, Bishop TF, Friderici J, Kleppel R, Lindenauer PK. The cost of defensive medicine on 3 hospital medicine services. JAMA Intern Med. 2014;174(11):1867-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.4649
Raab EL. The parameters of informed consent. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 2004;102:225-32.
Long Island Personal Injury Law Firm | Palermo Law, P.L.L.C. I signed an informed consent form – can I still sue for medical malpractice? Available from: https://thesuffolkpersonalinjurylawyer.com/signed-consent-form-can-sue-medical-malpractice/. Cited Aug 24, 2021.
Mello MM, Frakes MD, Blumenkranz E, Studdert DM. Malpractice liability and health care quality: a review. JAMA. 2020;323(4):352-366. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.21411
Ronquillo Y, Robinson KJ, Nouhan PP. Expert witness. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing.
Becker's Hospital Review. More than 50% of physicians have been sued for malpractice, study finds. Available from: https://www.beckershospitalreview.com/hospital-physician-relationships/more-than-50-of-physicians-have-been-sued-for-malpractice-study-finds.html. Cited Aug 24, 2021.
Pandey U. Knowledge of medical negligence among medical students. Innovare J Med Sci. 2014;2(4):1-2.
Rai JJ, Acharya RV, Dave D. Knowledge and awareness among interns and residents about medical law and negligence in a medical college in Vadodara – A questionnaire study. IOSR J Dent Med Sci. 2013;3(40):32-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.9790/0853-0343238
Sivasuthan S, Babu B, Varghese A, David A. Awareness of 3rd semester MBBS students regarding the medico-legal issues in our society and the need for training in forensic medicine – A descriptive cross-sectional study. J Evol Med Dent Sci. 2018;7(36):401-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.14260/jemds/2018/897
Roy AD, Chen L, Santucci K. What do pediatric residents know about malpractice?. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2011;27(7):586-90. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/PEC.0b013e31822251fb
Chen WT, Fu CP, Chang YD, Shiao YC, Chen PY, Wang CC. Developing an innovative medical ethics and law curriculum-constructing a situation-based, interdisciplinary, court-based learning course: a mixed methods study. BMC Med Educ. 2022;22(1):284. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-022-03349-z
Preston-Shoot M, McKimm J, Kong WM, Smith S. Readiness for legally literate medical practice? Student perceptions of their undergraduate medico-legal education. J Med Ethics. 2011;37(10):616-22. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1136/jme.2010.041566
Emanuel EJ. Reforming american medical education. Milbank Q. 2017;95(4):692-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/1468-0009.12291
Rehm SJ, Borden BL. The emotional impact of a malpractice suit on physicians: Maintaining resilien. Cleve Clin J Med. 2016;83(3):177-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3949/ccjm.83a.16004
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Nia Nikkhahmanesh, Paul Kang, Eric vanSonnenberg

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- The Author retains copyright in the Work, where the term “Work” shall include all digital objects that may result in subsequent electronic publication or distribution.
- Upon acceptance of the Work, the author shall grant to the Publisher the right of first publication of the Work.
- The Author shall grant to the Publisher and its agents the nonexclusive perpetual right and license to publish, archive, and make accessible the Work in whole or in part in all forms of media now or hereafter known under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License or its equivalent, which, for the avoidance of doubt, allows others to copy, distribute, and transmit the Work under the following conditions:
- Attribution—other users must attribute the Work in the manner specified by the author as indicated on the journal Web site; with the understanding that the above condition can be waived with permission from the Author and that where the Work or any of its elements is in the public domain under applicable law, that status is in no way affected by the license.
- The Author is able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the nonexclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the Work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), as long as there is provided in the document an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post online a prepublication manuscript (but not the Publisher’s final formatted PDF version of the Work) in institutional repositories or on their Websites prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work. Any such posting made before acceptance and publication of the Work shall be updated upon publication to include a reference to the Publisher-assigned DOI (Digital Object Identifier) and a link to the online abstract for the final published Work in the Journal.
- Upon Publisher’s request, the Author agrees to furnish promptly to Publisher, at the Author’s own expense, written evidence of the permissions, licenses, and consents for use of third-party material included within the Work, except as determined by Publisher to be covered by the principles of Fair Use.
- The Author represents and warrants that:
- the Work is the Author’s original work;
- the Author has not transferred, and will not transfer, exclusive rights in the Work to any third party;
- the Work is not pending review or under consideration by another publisher;
- the Work has not previously been published;
- the Work contains no misrepresentation or infringement of the Work or property of other authors or third parties; and
- the Work contains no libel, invasion of privacy, or other unlawful matter.
- The Author agrees to indemnify and hold Publisher harmless from the Author’s breach of the representations and warranties contained in Paragraph 6 above, as well as any claim or proceeding relating to Publisher’s use and publication of any content contained in the Work, including third-party content.
Enforcement of copyright
The IJMS takes the protection of copyright very seriously.
If the IJMS discovers that you have used its copyright materials in contravention of the license above, the IJMS may bring legal proceedings against you seeking reparation and an injunction to stop you using those materials. You could also be ordered to pay legal costs.
If you become aware of any use of the IJMS' copyright materials that contravenes or may contravene the license above, please report this by email to contact@ijms.org
Infringing material
If you become aware of any material on the website that you believe infringes your or any other person's copyright, please report this by email to contact@ijms.org







